UNDERSTANDING THE IMPORTANCE OF NUTRITION FOR BREASTFEEDING MOTHERS

THE ROLE OF DIET IN MATERNAL HEALTH
A balanced diet is very important for breastfeeding mothers because it helps keep them healthy and full of energy. Eating nutritious foods not only helps moms recover from childbirth but also supports the production of good-quality breast milk for their babies. When moms eat well, it can improve their mood and reduce stress, which is especially helpful during the challenging first months after giving birth. A healthy diet provides enough calories and essential nutrients that the body needs. It also helps prevent common postpartum problems like anemia (low iron) and mood swings. That’s why it’s important for breastfeeding moms to eat a wide variety of foods from all the main food groups every day.
KEY NUTRIENTS FOR OPTIMAL MILK PRODUCTION
-
Protein:
Protein is essential for repairing tissues and building strong muscles. It also supports the growth and development of your baby through breast milk.
-
Calcium:
Calcium helps keep your bones and teeth strong. It’s also important for your baby’s bone development and is passed through breast milk.
-
Folate:
Folate (or folic acid) helps in making new cells and supports the healthy growth of your baby. It also helps prevent anemia in moms.
-
Vitamin D:
Vitamin D helps your body absorb calcium better and supports your baby’s bone and immune system development. It also contributes to your overall energy and mood.
THE IMPACT OF DIET ON BREASTFEEDING INFANTS
Toxins and Ingredients in Maternal Diets that Affect Babies
Breastfeeding mothers should be mindful of certain substances that can affect their babies. Caffeine, found in coffee, tea, and some sodas, may make babies restless and irritable if consumed in large amounts. Alcohol can interfere with a baby’s sleep and development, so it should be limited or avoided. Some fish, like shark, swordfish, and king mackerel, contain high levels of mercury, which can harm a baby’s developing nervous system. Additionally, pesticides from unwashed fruits and vegetables can pass into breast milk, so it's important to wash produce thoroughly before eating.

Allergies and Sensitivities: What to Watch Out For
Some babies may show sensitivity to certain foods their mothers eat while breastfeeding. Common allergens that can cause reactions include dairy, eggs, peanuts, tree nuts, soy, and wheat. If a baby is sensitive, they might show signs like fussiness, excessive gas, diarrhea, skin rashes, or nasal congestion. These symptoms can be uncomfortable for the baby and stressful for the mother. If food sensitivity is suspected, it's helpful to keep a food diary and consult a healthcare provider to identify and manage any triggers.
CREATING A SAFE AND HEALTHY BREASTFEEDING DIET
Tips for Choosing Safe and Nutritious Foods
-
Eat a variety of fruits and vegetables:
Fruits and veggies are rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that support your health and help produce nutritious breast milk for your baby.
-
Choose whole grains over refined grains:
Whole grains like brown rice, oats, and whole wheat bread provide more fiber and nutrients, keeping you fuller longer and supporting steady energy levels.
-
Include lean proteins like chicken, fish, and beans:
Lean proteins are essential for muscle repair and milk production. They also supply important nutrients like iron and omega-3 fatty acids.
-
Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water:
Drinking enough water helps maintain your milk supply and keeps you energized and refreshed throughout the day.
How to Prepare and Store Your Breastfeeding Diet
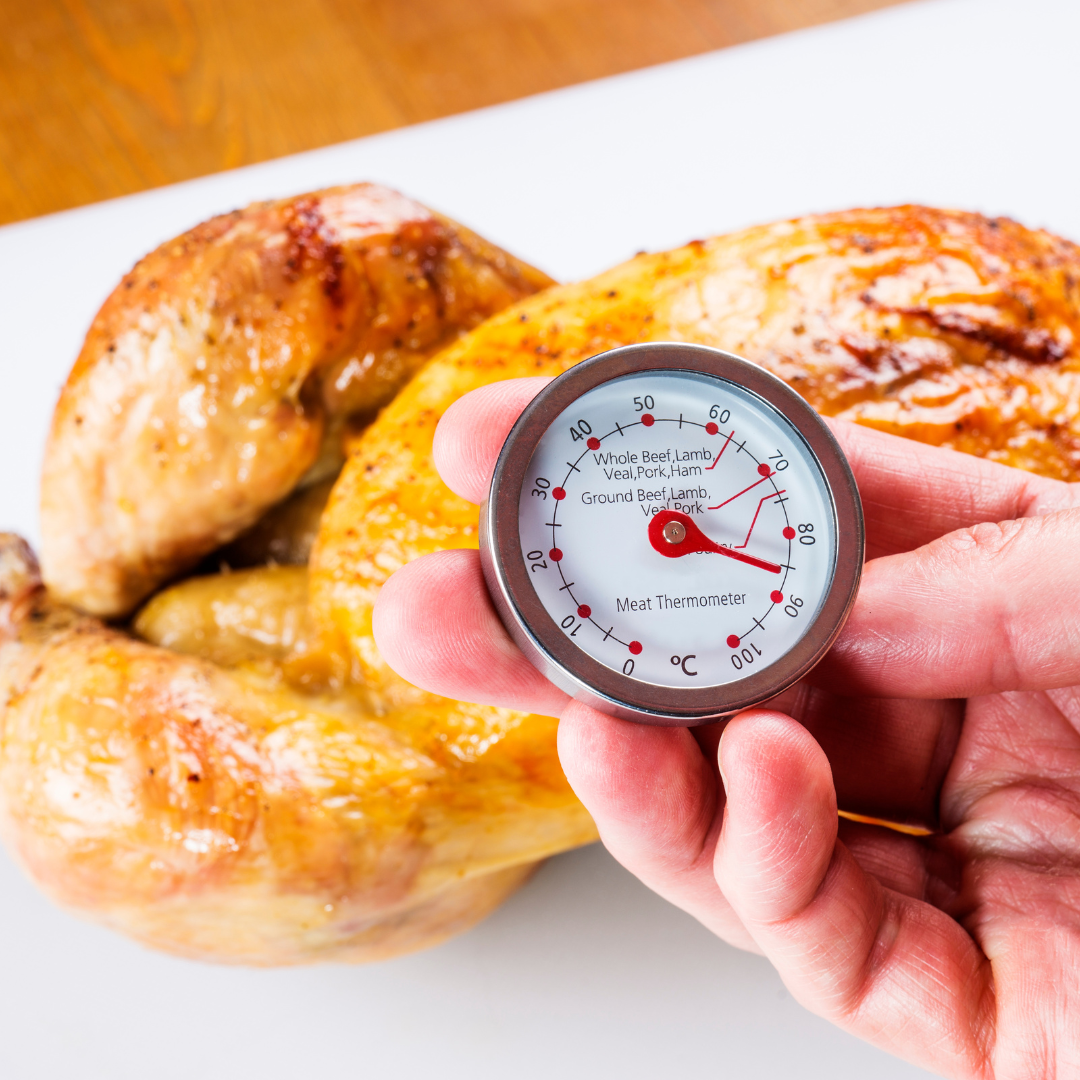
Safe food preparation is very important for breastfeeding moms to stay healthy and protect their babies. Always wash your hands before handling food to prevent germs. Cook meats thoroughly to the right temperature to kill harmful bacteria. Keep raw and cooked foods separate to avoid cross-contamination. Store leftovers in the refrigerator quickly to keep them fresh and use clean utensils and cutting boards every time. When it comes to storing breast milk, use clean, sterile containers and label them with the date and time. You can keep milk refrigerated for up to 4 days or freeze it for up to 6 months. When thawing frozen milk, do it slowly in the refrigerator rather than at room temperature to keep it safe for your baby.

The Role of Health Supplements and Vitamins in Pregnancy and Nursing
Many doctors advise breastfeeding mothers to continue taking prenatal vitamins to help fill any nutritional gaps in their diet. Common supplements recommended for nursing moms include multivitamins, calcium, vitamin D, and omega-3 fatty acids, which support both the mother’s health and the baby’s development. However, it’s important to always talk to your doctor before starting any supplements, as some may not be safe during breastfeeding. Your healthcare provider can suggest the best options based on your individual needs. Remember, supplements are meant to complement a balanced diet, not replace healthy eating habits.
In conclusion, a healthy diet is crucial for breastfeeding mothers and their babies. By avoiding certain foods and choosing nutritious options, you can support your health and your baby's growth. Always consult with your healthcare provider for personalized advice on breastfeeding nutrition.